We’ve all heard the myths — that what our canine friends lack in vision they make up for in their other senses. Early research seemed to show that dogs see in only black and white, though not much more was known until recently. Dog eyesight is different than humans’, to be sure, but not everything you’ve heard is true. In fact, your best furry friend may be able to see more than you think.
Dog color blindness is absolutely real, but it’s not as simple as black, white, and gray. Keep on reading to find out what colors dogs can see, how their eyes work, and other visual differences between canines and humans.
Finally! It’s time to see the world through your pup’s eyes.
Do dogs see in black and white?
Contrary to popular belief, dogs do not actually see exclusively black and white. Instead of the complete lack of color, dog colorblindness is more similar to the red-green color blindness that humans can experience (via Purina). It all comes down to the anatomy of the canine eye, which all in all is not that different from the human eye.
So why is dog eyesight different?
Anatomy of the eye
When it comes to color, the retina is where it’s at. This is the part of the eye that contains rods and cones — the photoreceptive cells that capture light and send signals to the brain. Rods, according to Arizona State University, assist in night vision and low-level light, though they do not reflect or absorb any color. Cones, on the other hand, need a much higher level of light and help the eye see color.
Knowing what you now know, you may not be surprised to find out that dogs’ eyes have many more cones than rods (via American Kennel Club). People, though, have more cones than rods, which allows us to see many more colors than dogs can. Still, dogs have some cones, even if it’s only two types compared to humans’ three types. This is what makes canine color perception so limited.
Because canines have more rods than humans do in their retinas, dogs are more easily able to see in dim light, especially when detecting motion. You can thank evolution for this helpful trait since dogs were nocturnal hunters in the wild (via AKC).

What colors do dogs see?
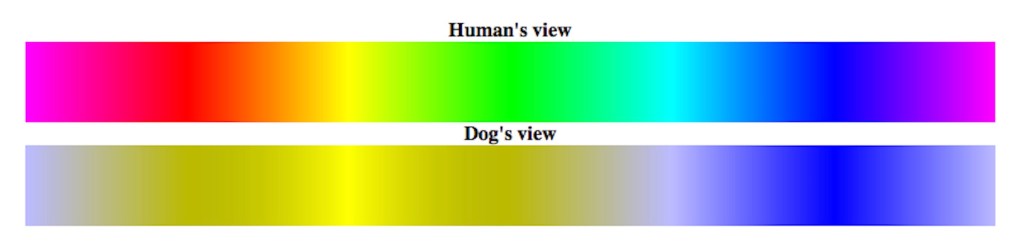
Dogs are missing the type of cone that helps the brain make sense of red and green, so those colors are absent to them. Instead of seeing red, notes Ryan Llera, BSc, DVM, and Lynn Buzhardt, DVM with VCA Hospitals, your furry friend will see a shade of brown, gray, or even black; and instead of green or orange, they’ll see a yellowish color.
To help pet parents and animal lovers get an even better idea of what a dog sees, neuroscientist András Péter developed Dog Vision. This website shows side-by-side comparisons of human and canine vision color ranges, brightness spectrums, and even sharpness. Take a look — can your fur baby see more than you thought they could?
Does breed affect vision?
It’s no surprise that a dog’s breed affects certain characteristics, like their height, movement, and even respiratory health, but did you know it can change their vision, too? The folks at Purina credit Bonnie Beaver, author of Canine Behavior: A Guide for Veterinarians, for explaining how a dog’s face shape can affect the way they see. It may not change any of their color perceptions, but can make their entire field of vision different than other pups:
“For example, a dog with a narrow face and long nose, such as a Borzoi, has a narrow field of binocular focus and a larger field of peripheral vision. A brachycephalic breed, on the other hand, such as a Pekingese, has a wider area of binocular vision, but an even bigger blind spot.”
So don’t get discouraged next time your dog can’t seem to find a toy that’s right in front of him — he may not be able to see it! Perhaps the toy is red or orange, making it hard to see; or maybe the toy just landed in your dog’s blind spot. When in doubt, grab a yellow or blue toy to help them keep their eye on it — and don’t forget a little encouragement!



